Part: 1: Flux Paints and Pastes – Part 1
Flux and Braze Paste Characteristics
The purpose of flux and/or braze pastes is to provide an initial or supplemental volume of flux and/or filler metal in the form of a viscous liquid at or near the interface of two components:
- Folded tube seams
- Tube to header joints
- Connector tube to manifolds
- End caps
- Blocks and fittings
- Flame braze joints
Viscosity
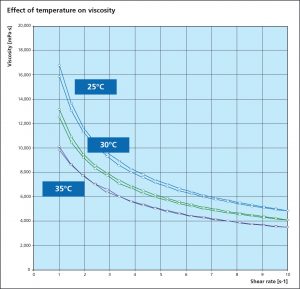
Flux and braze pastes exhibit pseudoplastic viscosity, meaning to have shear thinning behavior. As the shear stress is increased, the viscosity decreases, but the relationship is not linear. When the shear stress decreases, the viscosity increases, again non-linearly. Other factors affecting viscosity are solids content and temperature. Generally speaking, as the temperature increases, the viscosity decreases. Conversely, as the solids content increases, the viscosity also increases. These dependences illustrate the importance of quoting the parameters under which the viscosity is measured.
The graph below shows the effect of temperature on viscosity:
Note that at each temperature, a double curve is shown representing two sets of measurements: one curve shows the decrease in viscosity as the shear rate is increased and the other curve shows the increase in viscosity as the shear rate is decreased. This mirrored behavior as the shear rate is increased or decreased perfectly illustrates the pseudoplastic behavior.
The following curves show both: – the effect of temperature, and – solids content on viscosity:

These properties allow a bead of flux paste to be dispensed on the surface of a folded tube consistently and continuously at line speeds ranging from 30 m/min to 120 m/min.

Influence of Carrier on Volatilization Behavior
Since the carrier is a main ingredient, the carrier burn off temperature must be considered.
Below are 3 TGA curves showing burn-off temperature of 3 different paste formulations:
Delivery Systems and Recommendations
When designing a flux delivery system, choosing the right delivery pump is just as important. Below is a list of pros and cons for the associated pumps.
Diaphragm Pump
- Low cost, low maintenance
- High flow
- Generally used for low viscosity fluids
- Pulsation, viscosity sensitive
- Poor flow metering
Air Over Liquid (Pressure Vessel)
- Low cost, low maintenance
- Temperature sensitive
- Viscosity sensitive
- Poor flow metering
Rotary/Gear Pump
- High viscous liquids
- Metered dosing
- Pulsation
- Does not handle solids
Rotor-Stator Pumps
- High viscous liquids
- No pulsation
- Precision metering
- Not viscosity sensitive
- Highest cost
Rotor-stator pumps are the pumps of choice because of their ability to deliver a constant volume of material without pulsation over a range of flow rates. The best example of this is in the localized dispensing of a continuous bead/stripe in folded tube mills where speeds can range from 20 m/min to 120 m/min.
In lower demanding applications where precision dispensing and flow control is not so critical, for example in tube to header fluxing, the lower cost options (air over liquid, diaphragm pumps) are more than adequate.