HF can potentially be formed during the flux brazing process. HF is very toxic, irritating to the eyes, skin and respiratory tract and cause severe burns of the skin and eyes. The threshold limit value (TLV) for HF is a ceiling concentration of 3 ppm (2.3 mg/m3), a concentration that should not be exceeded during any part of the working shift.
Drying ovens can be electrically heated or gas fired. In gas fired drying ovens, it is possible that any flux particles entrained in the moist air and passed through the high temperature flames may generate HF. The concern here is not so much with employee exposure, but that HF may be released into the atmosphere.
Similarly, flux particles coming in contact with the hot flames in a flame brazing station may also generate HF. Suitable local exhaust systems must be in place to capture vapors and fumes that may contain HF.
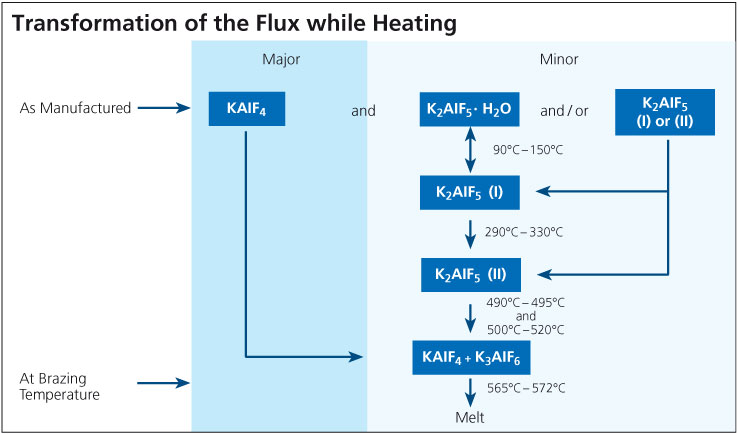
It is known that one of the components of the flux, KAlF4, has a measurable vapor pressure and the rate of evaporation increases rapidly once the flux is molten. With regard to CAB brazing (furnace brazing) where traces of moisture are always present even at below –40°C dew point, a number of compounds can be formed in the system K – Al – F – H – O. To our knowledge there has been no academic effort to create a thermodynamic model of this system. Thus, it is impossible to predict which compounds will and will not exist, and in what temperature or humidity regimes. This is why more than one mechanism has been proposed for the generation of HF, but no unique reaction mechanism has been identified:
3KAlF4 + 3H2O → Al2O3 + K3AlF6 + 6HF
2KAlF4 + 3H2O → 2KF + Al2O3 + 6HF
While the evidence above points to gas phase reactions between flux fumes and water vapor for the generation of HF, Thompson and Goad1) proposed that AlF3 dissolved in the flux melt is subject to hydrolysis according to:
2AlF3 + 3H2O → Al2O3 + 6HF
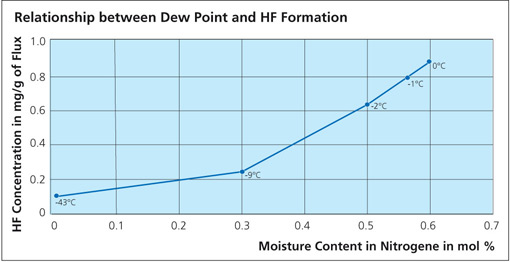
What is clear is that in all cases, HF is shown as a reaction product. As for the quantity, Field and Steward2) have indicated that the amount of HF formed is typically 20 ppm in the exhaust of a continuous tunnel furnace. Solvay’s own research work showed that even when flux on aluminum is heated in a bone-dry nitrogen atmosphere, a small quantity of HF is still generated3). A source of hydrogen must be made available for HF to be formed even under bone-dry conditions and this might include reduction of aluminum hydroxide, degassing of furnace walls, leakage or other less obvious sources. The work showed that even under ideal conditions, it is virtually impossible to avoid some HF formation. The graph below shows the relationship between dew point and HF formation:
The amount of HF generated depends on several factors such as:
- Flux load going through the furnace – flux loading and component throughput
- Temperature profile – heating rate and time at temperature
- Furnace atmosphere conditions such as nitrogen flow and dew point
The HF is exhausted together with the nitrogen stream and absorbed by the dry scrubber.
1) Thompson, W.T., Goad, D.W.G., Can. J. Chem., 1976, Vol. 54, p3342-3349
2) Steward N.I., Field D.J., SAE 870186, 1987
3) Lauzon, D.C., Belt, H.J., Bentrup, U., Therm Alliance Seminar, Detroit, 1998