Thermal management of electric vehicles is faced with challenges, as batteries need to be kept at a defined temperature range between 15°C and 35°C in order to function at peak performance throughout the life of a vehicle. The manufacture of such battery cooling systems involves controlled atmosphere brazing technology using noncorrosive flux. OEMs develop different battery cooler designs that require adapted fluxing methods.
Thermal management of electric vehicles is faced with challenges, as batteries need to be kept at a defined temperature range between 15°C and 35°C in order to function at peak performance throughout the life of a vehicle. The manufacture of such battery cooling systems involves controlled atmosphere brazing technology using noncorrosive flux. OEMs develop different battery cooler designs that require adapted fluxing methods.
During recent years, gel blockage in engine coolant systems with aluminum heat exchangers produced by CAB has gotten more and more attention in the automotive industry. A general understanding of gel formation processes in engine coolants and the role that flux residues on internal surfaces of brazed heat exchangers may or may not have is of significant interest.
Brazing Issues
Folded tubes (or B-type tubes) for radiators have been developed several years ago. There are slightly different designs patented by most of the heat exchanger manufacturers.
Below illustrations show three different B tube designs:
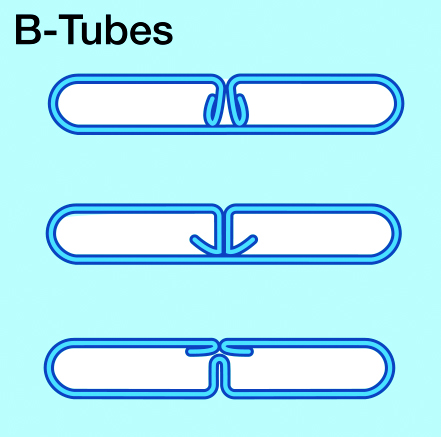
The folded tubes are produced from brazing sheet coils by a multi-step roll forming process – bringing the sheet gradually into a “B” shape. B-tubes have certain advantages – particularly regarding strength. The folded ends of the tube sheet are brazed inside the tube, which creates a very robust bridge between the walls. This results in higher burst pressure resistance.
The B tube roll forming process replaces the tube seam welding procedure. Standard flat radiator tubes are seam welded on one side – while folded tubes are joined during brazing. It is a general observation that folded tubes (“B-tubes”) are more difficult to braze (when compared with seam welded tubes).
Some of the problems are related to flux coverage. Other difficulties are related to erosion effects due to the fact that there is more filler metal available from folded tubes than from welded tubes. One common feature of all folded tubes designs is the presence of a triangular gap or “delta” between the flat exterior portion of the tube wall surface and the fin convolution. This delta is created by the presence of the folds in the tube. This is a common failure site at the tube to header joint because there is not enough filler metal at the joint to allow for proper fillet formation.
In order to avoid troublesome inner tube fluxing and to minimize the level of flux residue in the cooling loop it has become more and more common to flux the tube folds (the so called leg) at the folding machine using a needle like dispenser which places a thin bead of flux paste along where the tube leg touches the tube inner surface in the subsequent folding operation. A specially formulated flux paste is required for such operation. Solvay offers for this purpose several formulations with different flux concentrations, viscosity ranges, and additives.
Another common feature with folded tube designs is that the fin-to-tube-joints are consistently larger on the folded tube side than on the non-folded side of the tube. This is attributed to the path created by the fold in the tube which allows the filler metal to flow from the header, up the tube and from the tube fold panels up into the fin to tube joint.
The dominant phenomenon present in brazing is capillarity, i.e. the force which draws the filler metal into the joints. A heat exchanger core may be considered as a complex matrix of capillary sites. Now, in a non-folded tube design, all the joints are considered separate and autonomous, that is none of the joints are connected. For the most part then, filler metal is drawn into the fin to tube and tube to header joints from the immediate area surrounding the joint.
When a folded tube is added, many of the previously separated joints become connected and inter-dependent. The fin to tube joints on the side of the tube fold are now in direct contact with the seam along the fold of the tube, which is also in contact with the tube to header joint at the header slot. Now, the heat exchanger has an extended zone to draw filler metal from, as the available clad for the fin to tube joint now extends throughout the entire length of the tube seam and even includes the header. During brazing, the center of the core will heat up faster (lighter weight compared to the heavier thermal mass of the headers and side supports) and creates a temperature gradient. The filler metal from the header is able to travel down the seam throughout the length of the seam, depleting the area around the tube to header joint of valuable filler metal. The result is smaller tube to header joints with a greater risk of failure and large tube to fin joints on the folded side of the tube.
One way to reduce the flow of filler metal along the seam resulting in saturation of the tube to fin joints is by putting Mg in the fin. This goes back to the principle of competing joints, where the joint with more Mg will draw less filler metal. By adding a small percentage of Mg in the fin yet keeping it brazeable, the wettability of the fin to tube joint is slightly reduced. The fin-to-tube-joints neither draw up all of the available clad from the headers nor from the tube seams. The clad no longer runs up the tube. Reduced wettability forces the clad to stay in the tube seam and in the tube to header joints.
If problems are observed with excessively large tube to fin joints on the folded tube side and/or if the tube to header joints are small and commonly fail due to a lack of filler metal, it may be considered to use fins with more Mg – to take advantage of the features mentioned above.
Technical Information by Leszek Orman, Hans-Walter Swidersky and Daniel Lauzon
Abstract
For just as long as aluminium has been used for brazing heat exchangers, there has been a trend to down-gauging components for weight savings. The most common alloying element to achieve higher strength alloys for the purpose of down-gauging is magnesium. While magnesium additions are helpful in achieving stronger alloys, the consequence is a decrease in brazeability. This article discusses the mechanism of brazing deterioration with the addition of magnesium and proposes the use of caesium compounds as a way of combating these effects.
We split the article in five parts:
- Introduction
- Effects of Mg on the Brazing Process
- Mechanism of Magnesium Interaction with the Brazing Process
- Caesium Fluoroaluminates
- NOCOLOK® Cs Flux
NOCOLOK® Cs Flux
As a more practical means of obtaining better brazeability of Mg containing alloys, a mixture of standard NOCOLOK® Flux and caesium fluoroaluminates is used. The positive influence of Cs on brazing magnesium containing alloys was previously reported in a patent for a product where potassium fluoroaluminates were mixed with caesium fluoroaluminates [11]. However, this patent covered a rather wide ratio of potassium fluoroaluminates to caesium fluoroaluminates.
The influence of actual elemental Cs content on brazeability was investigated by Garcia et al [12]. Brazeability was determined by the length of the joint obtained in a system with a gradual increase in gap clearance (similar in concept to the one shown in Fig. 1). In their work they used 6063 alloy with a Mg content of 0.66 wt%. Their major finding is presented in Fig. 6.
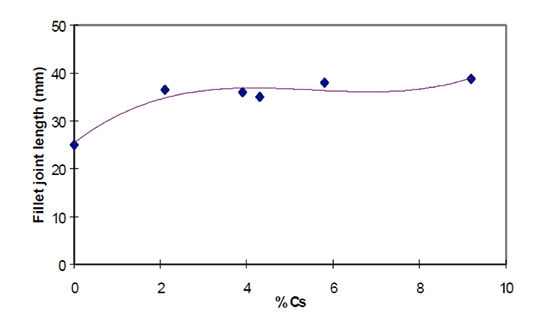
Fig. 6: Brazeability of AA6063 alloy as a function of caesium content at flux load of 5 g/m2 [12].
As seen in Fig. 5, even a relatively low concentration of Cs in the flux mixture improves brazeability of an alloy containing 0.66 wt% Mg. An increase of Cs concentration above 2 wt% does not lead to further improvement in brazeability. In his work Garcia et al also confirmed that faster heating rates, though positive do not significantly influence brazeability.
This work led to another important finding. By brazing small sample radiators in an industrial type furnace, Garcia et al established a practical threshold for Mg content. The flux containing 2 wt% Cs is effective for brazing aluminium alloys with 0.35% to 0.5 % Mg. At lower levels of magnesium no difference between the standard flux and the 2 wt% Cs flux was observed. Brazing samples containing 0.66% of magnesium yielded leak free parts – but the brazing ratio for fins was not fully satisfactory.
This work led to the standardization of Solvay’s NOCOLOK® Cs Flux at 2 wt% Cs. By using this minimal but effective Cs concentration in the mixture, the chemical and physical characteristics are similar to the standard flux.
Summary
- Magnesium is very often added to aluminium alloys to increase strength and machinability.
- The addition of magnesium negatively influences the brazing process due to the formation of smaller fillets and the presence of porosity in the joints. This is due to (a) magnesium diffusing to the surface during the brazing cycle and forming Mg containing oxides which are more difficult to remove by the molten flux and (b) by poisoning the action of flux through the formation of K-Mg-F compounds.
- The above effect can be made less pronounced when standard NOCOLOK® Flux is mixed with a caesium aluminium fluoride complex. At a concentration of 2 wt% Cs one can observe a positive effect on aluminium alloys containing magnesium. Increasing the Cs content above 2 wt% does not yield any further increase in brazeability.
- NOCOLOK® Cs Flux works effectively for alloys containing roughly 0.3 to 0.5 wt% Mg. Depending on specific design and process conditions, Cs containing fluxes can also offer benefits for alloys containing 0.3 wt% or even less Mg. For concentrations higher than 0.5 wt% of Mg, the effectiveness of Cs compounds in non-corrosive fluxes gradually decreases.
- Pure caesium aluminium fluoride complex is effectively used for flame brazing where a lower melting point flux is required.
Download the complete article as a PDF-File.
References:
- S. W. Haller, “A new Generation of Heat Exchanger Materials and Products”, 6th International Congress “Aluminum Brazing” Düsseldorf, Germany 2010
- R. Woods, “CAB Brazing Metallurgy”, 12th Annual International Invitational Aluminum Brazing Seminar, AFC Holcroft, NOVI, Michigan U.S.A. 2007
- T. Stenqvist, K. Lewin, R. Woods “A New Heat-treatable Fin Alloy for Use with Cs-bearing CAB flux” 7th Annual International Invitational Aluminum Brazing Seminar, AFC Holcroft, NOVI, Michigan U.S.A. 2002
- R. K. Bolingbroke, A. Gray, D. Lauzon, “Optimisation of Nocolok Brazing Conditions for Higher Strength Brazing Sheet”, SAE Technical Paper 971861, 1997
- M. Yamaguchi, H. Kawase and H. Koyama, ‘‘Brazeability of Al-Mg Alloys in Non Corrosive Flux Brazing’’, Furukawa review, No. 12, p. 139 – 144 (1993).
- A. Gray, A. Afseth, 2nd International Congress Aluminium Brazing, Düsseldorf, 2002
- H. Johansson, T. Stenqvist, H. Swidersky “Controlled Atmosphere Brazing of Heat Treatable Alloys with Cs Flux” VTMS6, Conference Proceedings, 2002
- U. Seseke-Koyro ‘‘New Developments in Non-corrosive Fluxes for Innovative Brazing’’, First International Congress Aluminium Brazing, Düsseldorf, Germany, 2000
- K. Suzuki, F. Miura, F. Shimizu; United States Patent; Patent Number: 4,689,092; Date of Patent: Aug. 25, 1987
- L. Orman, “Basic Metallurgy for Aluminum Brazing”, Materials for EABS & Solvay Fluor GmbH 11th Technical Training Seminar – The Theory and Practice of the Furnace and Flame Brazing of Aluminium, Hannover, 2012
- K. Suzuki, F. Miura, F. Shimizu; United States Patent; Patent Number: 4,670,067; Date of Patent: Jun. 2, 1987
- J. Garcia, C. Massoulier, and P. Faille, „Brazeability of Aluminum Alloys Containing Magnesium by CAB Process Using Cesium Flux,“ SAE Technical Paper 2001-01-1763, 2001
Technical Information by Leszek Orman, Hans-Walter Swidersky and Daniel Lauzon
Abstract
For just as long as aluminium has been used for brazing heat exchangers, there has been a trend to down-gauging components for weight savings. The most common alloying element to achieve higher strength alloys for the purpose of down-gauging is magnesium. While magnesium additions are helpful in achieving stronger alloys, the consequence is a decrease in brazeability. This article discusses the mechanism of brazing deterioration with the addition of magnesium and proposes the use of caesium compounds as a way of combating these effects.
We split the article in five parts:
- Introduction
- Effects of Mg on the Brazing Process
- Mechanism of Magnesium Interaction with the Brazing Process
- Caesium Fluoroaluminates
- NOCOLOK® Cs Flux
Caesium Fluoroaluminates
Magnesium is an extremely reactive element and therefore even a small amount of oxygen will cause its oxidation. In standard brazing furnaces most often the level of oxygen in the furnace atmosphere at the temperature ranges below brazing could be relatively high. Thus the formation of magnesium oxides seems to be inevitable. On the other hand, one can think about neutralizing or inhibiting the formation of the poisoning potassium magnesium fluoride compounds mentioned earlier. The formation of those compounds can be reduced in the presence of caesium fluoroaluminate compounds
Caesium fluoroaluminates exist in several compositions and crystallographic states such as CsAlF4, Cs[AlF4 (H2O)2], Cs2AlF5, Cs2AlF5 H2O, Cs3AlF6. The Cs compound commonly used for aluminium brazing contains mainly CsAlF4 and is also known as CsAlF – Complex.
Cs acts as a chemical scavenger for Mg. During the brazing process, caesium reacts with magnesium to form compounds such as CsMgF3 and/or Cs4Mg3F10 [8]. These compounds melt at lower temperatures than the filler metal. As such these compounds do not significantly interfere with aluminium brazing and allow the flux to retain much of its oxide dissolution and wetting capability.
The caesium fluoroaluminate complex has a low melting range (420 – 480°C), a high water solubility (~20 g/l at 20°C), and contains between 54 – 59 % of elemental caesium. Though there are literature references for using the pure Cs-complex as a brazing flux [9], the chemical characteristics present practical problems when one would like to replace standard NOCOLOK® Flux with pure caesium fluoroaluminates complex. The low melting range means that under normal CAB process conditions the flux would essentially dry out by evaporation before reaching the brazing temperature (~ 600oC). Furthermore, the high content of Cs makes it prohibitively expensive as a replacement for standard NOCOLOK® Flux.
However the Cs complex does find a use in several applications such as flame and induction brazing and as a key component of flux paste formulations for specialty alloys. In some processes, mainly flame brazing of copper and aluminium, this complex is the state of the art [10].
Aluminium and copper form a low melting eutectic (546°C). This means that it is not possible to braze copper and aluminium in a CAB process using standard filler metal alloys having a melting range from 577°C to 605°C. It is however possible to join aluminium and copper by flame brazing, but it requires high degree of temperature control and a lower melting filler alloy is recommended. Zinc-aluminium alloys are commonly used for such applications. Lower melting range filler alloys require lower melting range fluxes and since flux consumption for flame brazing is relatively low, it is economically feasible to use a caesium fluoroaluminate complex such as CsAlF4.
Download the complete article as a PDF-File.
References:
- S. W. Haller, “A new Generation of Heat Exchanger Materials and Products”, 6th International Congress “Aluminum Brazing” Düsseldorf, Germany 2010
- R. Woods, “CAB Brazing Metallurgy”, 12th Annual International Invitational Aluminum Brazing Seminar, AFC Holcroft, NOVI, Michigan U.S.A. 2007
- T. Stenqvist, K. Lewin, R. Woods “A New Heat-treatable Fin Alloy for Use with Cs-bearing CAB flux” 7th Annual International Invitational Aluminum Brazing Seminar, AFC Holcroft, NOVI, Michigan U.S.A. 2002
- R. K. Bolingbroke, A. Gray, D. Lauzon, “Optimisation of Nocolok Brazing Conditions for Higher Strength Brazing Sheet”, SAE Technical Paper 971861, 1997
- M. Yamaguchi, H. Kawase and H. Koyama, ‘‘Brazeability of Al-Mg Alloys in Non Corrosive Flux Brazing’’, Furukawa review, No. 12, p. 139 – 144 (1993).
- A. Gray, A. Afseth, 2nd International Congress Aluminium Brazing, Düsseldorf, 2002
- H. Johansson, T. Stenqvist, H. Swidersky “Controlled Atmosphere Brazing of Heat Treatable Alloys with Cs Flux” VTMS6, Conference Proceedings, 2002
- U. Seseke-Koyro ‘‘New Developments in Non-corrosive Fluxes for Innovative Brazing’’, First International Congress Aluminium Brazing, Düsseldorf, Germany, 2000
- K. Suzuki, F. Miura, F. Shimizu; United States Patent; Patent Number: 4,689,092; Date of Patent: Aug. 25, 1987
- L. Orman, “Basic Metallurgy for Aluminum Brazing”, Materials for EABS & Solvay Fluor GmbH 11th Technical Training Seminar – The Theory and Practice of the Furnace and Flame Brazing of Aluminium, Hannover, 2012
- K. Suzuki, F. Miura, F. Shimizu; United States Patent; Patent Number: 4,670,067; Date of Patent: Jun. 2, 1987
- J. Garcia, C. Massoulier, and P. Faille, „Brazeability of Aluminum Alloys Containing Magnesium by CAB Process Using Cesium Flux,“ SAE Technical Paper 2001-01-1763, 2001
Technical Information by Leszek Orman, Hans-Walter Swidersky and Daniel Lauzon
Abstract
For just as long as aluminium has been used for brazing heat exchangers, there has been a trend to down-gauging components for weight savings. The most common alloying element to achieve higher strength alloys for the purpose of down-gauging is magnesium. While magnesium additions are helpful in achieving stronger alloys, the consequence is a decrease in brazeability. This article discusses the mechanism of brazing deterioration with the addition of magnesium and proposes the use of caesium compounds as a way of combating these effects.
We split the article in five parts:
- Introduction
- Effects of Mg on the Brazing Process
- Mechanism of Magnesium Interaction with the Brazing Process
- Caesium Fluoroaluminates
- NOCOLOK® Cs Flux
Mechanism of Magnesium Interaction with the Brazing Process
According to M. Yamaguchi et al [5], when magnesium diffuses to the surface during brazing, a chemical reaction takes place with the flux resulting in the generation of KMgF3.
The authors suggest the following equations to explain some of the chemical interactions between magnesium and K1-3AlF4-6 flux:
- 3 MgO + 2 KAlF4 → MgF2 + 2 KMgF3 + Al2O3 (a)
- 3 MgO + 2 KAlF4 → 2 MgF2 + K2MgF4 + Al2O3 (b)
- 3 MgO + 2 K3AlF6 > → 3 K2MgF4 + Al2O3 (3)
By performing XRD (X-ray Diffraction) phase identification on products brazed with Mg containing alloys, A. Gray et al [6] confirmed the presence of K2MgF4, spinel oxide (Al2MgO4) and possibly KMgF3. These magnesium containing compounds have a characteristic needle like morphology as shown in Fig. 5.
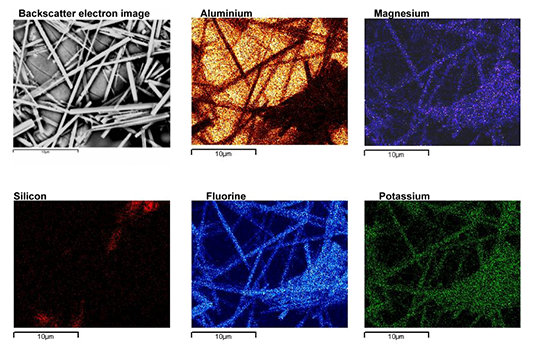
Fig. 5: Morphology of magnesium containing compounds as seen by Scanning Electron Microscope [6].
H. Johansson et al [7] also determined that at temperatures above 425°C the magnesium diffusion to the surface is very rapid resulting in the formation of magnesium oxide (MgO) and spinel oxides (Al2MgO4). These oxides have very low solubility in NOCOLOK® Flux. Subsequently these magnesium oxides react with the flux resulting in the formation of magnesium fluoride (MgF2) and potassium magnesium fluorides (KMgF3, K2MgF4, see equations a), b), and c)). These reactions change the flux chemical composition causing its melting range to rise. The melting point of these magnesium fluorides is very high, which in turn drives the melting point of the flux upwards, thereby decreasing the activity of the flux. The above factors also cause a decrease in the flowing characteristics of the flux thus lowering its overall effectiveness. Therefore the desired key point to limit the flux poisoning effect would be to reduce the formation of magnesium oxides and potassium magnesium fluorides.
Download the complete article as a PDF-File.
References:
- S. W. Haller, “A new Generation of Heat Exchanger Materials and Products”, 6th International Congress “Aluminum Brazing” Düsseldorf, Germany 2010
- R. Woods, “CAB Brazing Metallurgy”, 12th Annual International Invitational Aluminum Brazing Seminar, AFC Holcroft, NOVI, Michigan U.S.A. 2007
- T. Stenqvist, K. Lewin, R. Woods “A New Heat-treatable Fin Alloy for Use with Cs-bearing CAB flux” 7th Annual International Invitational Aluminum Brazing Seminar, AFC Holcroft, NOVI, Michigan U.S.A. 2002
- R. K. Bolingbroke, A. Gray, D. Lauzon, “Optimisation of Nocolok Brazing Conditions for Higher Strength Brazing Sheet”, SAE Technical Paper 971861, 1997
- M. Yamaguchi, H. Kawase and H. Koyama, ‘‘Brazeability of Al-Mg Alloys in Non Corrosive Flux Brazing’’, Furukawa review, No. 12, p. 139 – 144 (1993).
- A. Gray, A. Afseth, 2nd International Congress Aluminium Brazing, Düsseldorf, 2002
- H. Johansson, T. Stenqvist, H. Swidersky “Controlled Atmosphere Brazing of Heat Treatable Alloys with Cs Flux” VTMS6, Conference Proceedings, 2002
- U. Seseke-Koyro ‘‘New Developments in Non-corrosive Fluxes for Innovative Brazing’’, First International Congress Aluminium Brazing, Düsseldorf, Germany, 2000
- K. Suzuki, F. Miura, F. Shimizu; United States Patent; Patent Number: 4,689,092; Date of Patent: Aug. 25, 1987
- L. Orman, “Basic Metallurgy for Aluminum Brazing”, Materials for EABS & Solvay Fluor GmbH 11th Technical Training Seminar – The Theory and Practice of the Furnace and Flame Brazing of Aluminium, Hannover, 2012
- K. Suzuki, F. Miura, F. Shimizu; United States Patent; Patent Number: 4,670,067; Date of Patent: Jun. 2, 1987
- J. Garcia, C. Massoulier, and P. Faille, „Brazeability of Aluminum Alloys Containing Magnesium by CAB Process Using Cesium Flux,“ SAE Technical Paper 2001-01-1763, 2001
Technical Information by Leszek Orman, Hans-Walter Swidersky and Daniel Lauzon
Abstract
For just as long as aluminium has been used for brazing heat exchangers, there has been a trend to down-gauging components for weight savings. The most common alloying element to achieve higher strength alloys for the purpose of down-gauging is magnesium. While magnesium additions are helpful in achieving stronger alloys, the consequence is a decrease in brazeability. This article discusses the mechanism of brazing deterioration with the addition of magnesium and proposes the use of caesium compounds as a way of combating these effects.
We split the article in five parts:
- Introduction
- Effects of Mg on the Brazing Process
- Mechanism of Magnesium Interaction with the Brazing Process
- Caesium Fluoroaluminates
- NOCOLOK® Cs Flux
Effects of Mg on the Brazing Process
To illustrate the effects of Mg on the brazing process, Bolingbroke et al [4] chose the angle-on-coupon method. In this technique, an aluminium angle is laid on top of a cladded aluminium coupon where the legs of the angle are raised using stainless steel wire (see Fig. 1). Brazeability is thus measured as a function of the length of the fillet formed. In this set of experiments, the coupon base alloy is 3003 with Mg additions ranging from 0.1 to 0.58 w%. Only the coupon was fluxed at pre-defined loads ranging from 2 to 10 g/m2. The results of the Mg content on brazeability are shown in Fig. 2.
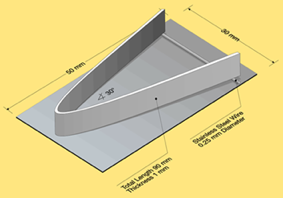
Fig. 1: Experimental set up for brazeability measurement [4].
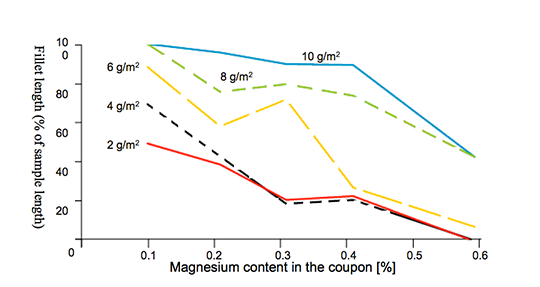
Fig. 2: Brazeability as a function of magnesium content [4].
Fig. 2 shows that increasing the flux load can reduce the negative influence of magnesium.
The solid state diffusion is time-temperature dependent and becomes rapid above 425°C. Thus brazing at higher heating rates should reduce the negative influence of Mg. The influence of heating rate on brazeability is shown in Fig. 3.
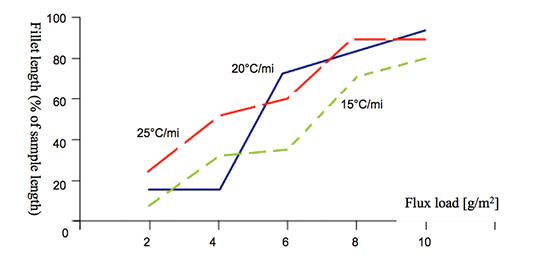
Fig. 3: Brazeability of 3003 alloy + 0.31 wt% Mg as a function of heating rate and flux load [4].
The influence of heating rates when kept within the values attainable for the CAB process is rather weak. Increasing the flux load is more effective in combating the negative influence of Mg for CAB processes.
In flame or induction brazing, where the heating rates are about two orders of magnitude higher than in the CAB process, alloys with Mg concentration even as high as 2% can be successfully brazed.
It should be noted that when one speaks of the brazing tolerance to Mg, it is always the total sum of the Mg concentrations in both components:
[Mg] component 1 + [Mg] component 2 = [Mg] total (1)
The effect of magnesium content on the appearance of the brazed joint is shown in Fig. 4.
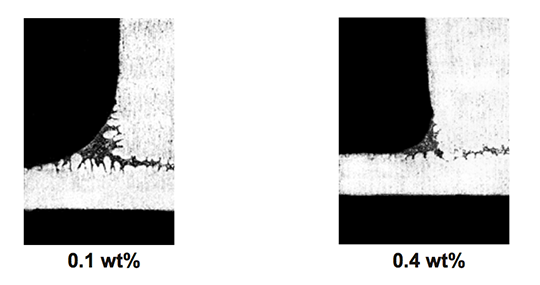
Fig. 4: Effect of Mg content on appearance of brazed joint [4].
At 0.1 wt% in the base coupon, the fillet is large and joining is complete. At 0.4 wt% Mg in the base coupon, the fillet volume is smaller.
Download the complete article as a PDF-File.
References:
- S. W. Haller, “A new Generation of Heat Exchanger Materials and Products”, 6th International Congress “Aluminum Brazing” Düsseldorf, Germany 2010
- R. Woods, “CAB Brazing Metallurgy”, 12th Annual International Invitational Aluminum Brazing Seminar, AFC Holcroft, NOVI, Michigan U.S.A. 2007
- T. Stenqvist, K. Lewin, R. Woods “A New Heat-treatable Fin Alloy for Use with Cs-bearing CAB flux” 7th Annual International Invitational Aluminum Brazing Seminar, AFC Holcroft, NOVI, Michigan U.S.A. 2002
- R. K. Bolingbroke, A. Gray, D. Lauzon, “Optimisation of Nocolok Brazing Conditions for Higher Strength Brazing Sheet”, SAE Technical Paper 971861, 1997
- M. Yamaguchi, H. Kawase and H. Koyama, ‘‘Brazeability of Al-Mg Alloys in Non Corrosive Flux Brazing’’, Furukawa review, No. 12, p. 139 – 144 (1993).
- A. Gray, A. Afseth, 2nd International Congress Aluminium Brazing, Düsseldorf, 2002
- H. Johansson, T. Stenqvist, H. Swidersky “Controlled Atmosphere Brazing of Heat Treatable Alloys with Cs Flux” VTMS6, Conference Proceedings, 2002
- U. Seseke-Koyro ‘‘New Developments in Non-corrosive Fluxes for Innovative Brazing’’, First International Congress Aluminium Brazing, Düsseldorf, Germany, 2000
- K. Suzuki, F. Miura, F. Shimizu; United States Patent; Patent Number: 4,689,092; Date of Patent: Aug. 25, 1987
- L. Orman, “Basic Metallurgy for Aluminum Brazing”, Materials for EABS & Solvay Fluor GmbH 11th Technical Training Seminar – The Theory and Practice of the Furnace and Flame Brazing of Aluminium, Hannover, 2012
- K. Suzuki, F. Miura, F. Shimizu; United States Patent; Patent Number: 4,670,067; Date of Patent: Jun. 2, 1987
- J. Garcia, C. Massoulier, and P. Faille, „Brazeability of Aluminum Alloys Containing Magnesium by CAB Process Using Cesium Flux,“ SAE Technical Paper 2001-01-1763, 2001
Technical Information by Leszek Orman, Hans-Walter Swidersky and Daniel Lauzon
Abstract
For just as long as aluminium has been used for brazing heat exchangers, there has been a trend to down-gauging components for weight savings. The most common alloying element to achieve higher strength alloys for the purpose of down-gauging is magnesium. While magnesium additions are helpful in achieving stronger alloys, the consequence is a decrease in brazeability. This article discusses the mechanism of brazing deterioration with the addition of magnesium and proposes the use of caesium compounds as a way of combating these effects.
We split the article in five parts:
- Introduction
- Effects of Mg on the Brazing Process
- Mechanism of Magnesium Interaction with the Brazing Process
- Caesium Fluoroaluminates
- NOCOLOK® Cs Flux
Introduction
Aluminium brazing using non-corrosive fluxes is the leading process for manufacturing automotive heat exchangers. Recently, this process has become more wide spread in the stationary Heating, Ventilation, Air-Conditioning and Refrigeration (HVAC&R) industry, both for domestic and commercial applications. The standard brazing process involves joining of components with a brazing alloy, typically an aluminium-silicon filler alloy. Al-Si brazing alloys have melting ranges from 577°C to 610°C, which is appreciably lower than the melting point range of the base aluminium alloys used for heat exchangers (630°C – 660°C). Fluoride-based non-corrosive fluxes of the system KF-AlF3 are used to displace the surface oxide film during the brazing process. A commonly used non-corrosive flux of the general formula K1-3AlF4-6 is known under the trademark name NOCOLOK® Flux with a melting range between 565°C and 572°C. The flux works by melting and disrupting the oxide film on aluminium, protecting the surfaces from re-oxidizing during brazing thus allowing the Al-Si brazing alloy to flow freely.
A consistent and on-going trend across all heat exchanger manufacturing sectors is towards lighter weight, accomplished by down-gauging of components. Also corrosion resistance is a key factor – particularly when there is no additional post brazing coating or treatment. These often contradictory trends call for aluminium alloys having higher and higher post brazed strength. While alloys from the 7xxx (alloyed with Zn) and 2xxx (alloyed with Cu) series can be precipitation hardened to the highest strengths of any aluminium alloys, their corrosion resistance without any additional coating is low and their solidus temperatures are below the melting range of currently used flux and filler metal combinations, and therefore they are not suitable for heat exchanger manufacturing by brazing.
The most common alloys used for aluminium brazing are from the 3xxx series (alloyed with Mn). After being subjected to the high temperature during the brazing cycle, these alloys have relatively low post-braze mechanical strength. Higher strength is offered by alloys from the 5xxx series (alloyed with 2 to 5 wt% Mg) where post brazed strengthening is achieved by solid solution hardening or by the 6xxx series (alloyed with Mg and Si) which can be precipitation hardened. A more comprehensive survey of mechanical properties of brazeable aluminium alloys is presented in [1]. It is worth observing that the brazing cycle itself could be considered as a thermal treatment for obtaining the precipitation hardening effect providing the cooling rate from the brazing temperature is sufficiently fast [2]. An example of such an alloy designated for specific use for aluminium brazed heat exchangers is described in detail in [3].
As well as increasing post-braze mechanical strength, the addition of Mg to certain alloys allows for improved machinability. Machining is necessary for heat exchanger components such as connecting blocks and threaded fittings.
There is however a certain limitation with the above mentioned alloys. They all contain magnesium. During the brazing cycle Mg negatively influences the process of oxide removal and it is generally accepted that Mg levels only up to 0.3% can be safely brazed with the standard brazing flux. This negative influence can be mitigated with the use of caesium containing compounds. The mechanism of Mg interference with the brazing process and the positive role of Cs additions to the flux in combating the effects of Mg are the subjects of the current paper.
To be continued soon…
Download the complete article as a PDF-File.
References:
- S. W. Haller, “A new Generation of Heat Exchanger Materials and Products”, 6th International Congress “Aluminum Brazing” Düsseldorf, Germany 2010
- R. Woods, “CAB Brazing Metallurgy”, 12th Annual International Invitational Aluminum Brazing Seminar, AFC Holcroft, NOVI, Michigan U.S.A. 2007
- T. Stenqvist, K. Lewin, R. Woods “A New Heat-treatable Fin Alloy for Use with Cs-bearing CAB flux” 7th Annual International Invitational Aluminum Brazing Seminar, AFC Holcroft, NOVI, Michigan U.S.A. 2002
- R. K. Bolingbroke, A. Gray, D. Lauzon, “Optimisation of Nocolok Brazing Conditions for Higher Strength Brazing Sheet”, SAE Technical Paper 971861, 1997
- M. Yamaguchi, H. Kawase and H. Koyama, ‘‘Brazeability of Al-Mg Alloys in Non Corrosive Flux Brazing’’, Furukawa review, No. 12, p. 139 – 144 (1993).
- A. Gray, A. Afseth, 2nd International Congress Aluminium Brazing, Düsseldorf, 2002
- H. Johansson, T. Stenqvist, H. Swidersky “Controlled Atmosphere Brazing of Heat Treatable Alloys with Cs Flux” VTMS6, Conference Proceedings, 2002
- U. Seseke-Koyro ‘‘New Developments in Non-corrosive Fluxes for Innovative Brazing’’, First International Congress Aluminium Brazing, Düsseldorf, Germany, 2000
- K. Suzuki, F. Miura, F. Shimizu; United States Patent; Patent Number: 4,689,092; Date of Patent: Aug. 25, 1987
- L. Orman, “Basic Metallurgy for Aluminum Brazing”, Materials for EABS & Solvay Fluor GmbH 11th Technical Training Seminar – The Theory and Practice of the Furnace and Flame Brazing of Aluminium, Hannover, 2012
- K. Suzuki, F. Miura, F. Shimizu; United States Patent; Patent Number: 4,670,067; Date of Patent: Jun. 2, 1987
- J. Garcia, C. Massoulier, and P. Faille, „Brazeability of Aluminum Alloys Containing Magnesium by CAB Process Using Cesium Flux,“ SAE Technical Paper 2001-01-1763, 2001
